Unveiling the Baltic countries – Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania – a region steeped in historical significance, cultural diversity, and remarkable economic growth. Embark on a journey to discover the captivating essence of these nations that have left an indelible mark on the European landscape.
From their ancient roots to their vibrant present, the Baltic countries have crafted a unique identity, blending the influences of East and West. Their strategic location on the Baltic Sea has shaped their destiny, fostering a rich maritime heritage and cultural exchange.
Historical Background
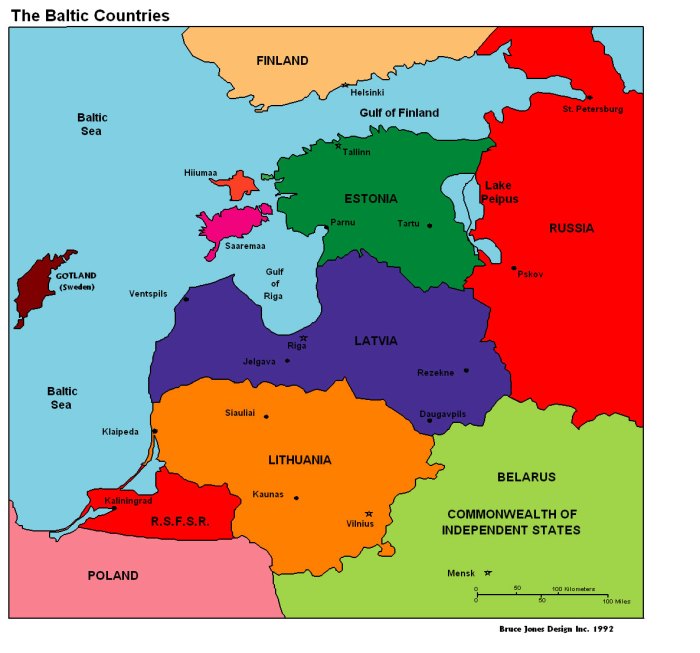
The Baltic countries, comprising Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania, possess a rich and complex history that has shaped their cultural identities and geopolitical landscapes. These nations have witnessed centuries of foreign rule, cultural exchange, and independence movements.
The Baltic countries, comprising Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania, are renowned for their rich history, stunning architecture, and breathtaking natural landscapes. These nations offer a captivating blend of culture, tradition, and modernity. While the Baltic countries hold a unique allure, it’s equally fascinating to explore the vibrant city of Chennai in India.
From its bustling markets to its historical landmarks, and chennai offers a captivating glimpse into the diverse cultural tapestry of the Indian subcontinent. As we delve deeper into the Baltic countries, we discover a region steeped in charm and intrigue.
The region’s cultural diversity is evident in its languages and traditions. Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania each have their own distinct languages, belonging to different language families: Estonian to the Finno-Ugric group, and Latvian and Lithuanian to the Baltic group of Indo-European languages. Despite their linguistic differences, the Baltic countries share a common cultural heritage, influenced by both Western and Eastern traditions.
Key Historical Events, Baltic countries
- 12th-13th centuries: Germanic crusaders establish control over the region, leading to the formation of the Livonian Order.
- 16th century: The Reformation spreads through the Baltic countries, leading to the establishment of Lutheranism as the dominant religion.
- 18th century: The Russian Empire gains control over the Baltic provinces.
- 19th century: National revival movements emerge in the Baltic countries, seeking independence from Russian rule.
- 1918: Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania declare independence.
- 1940: The Soviet Union annexes the Baltic countries.
- 1991: The Baltic countries regain independence after the collapse of the Soviet Union.
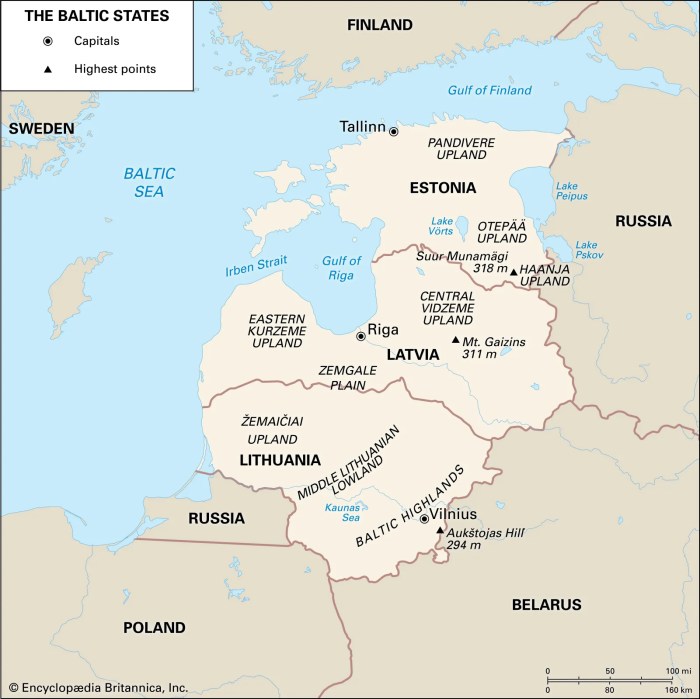
Geographic Features
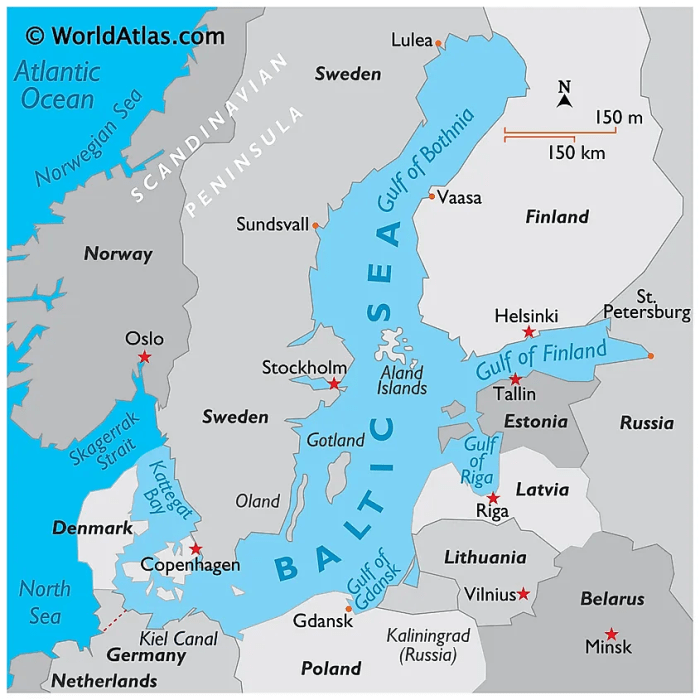
The Baltic countries of Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania are located in Northern Europe, bordering the Baltic Sea. The region has a predominantly flat landscape, with rolling hills and forests covering much of the area. The climate is temperate, with warm summers and cold winters. The region is rich in natural resources, including oil, gas, and timber.
Physical Characteristics
The following table compares the physical characteristics of the Baltic countries:
| Country | Area (km²) | Population (2021) | Capital |
|—|—|—|—|
| Estonia | 45,227 | 1,326,535 | Tallinn |
| Latvia | 64,589 | 1,894,424 | Riga |
| Lithuania | 65,300 | 2,794,700 | Vilnius |
Economic Development
Since regaining independence in 1991, the Baltic countries have experienced significant economic development, transforming from centrally planned economies to market-oriented ones.
Estonia has consistently outpaced its neighbors in terms of economic growth, with a GDP per capita of $27,314 in 2023, significantly higher than Latvia’s $19,185 and Lithuania’s $18,656.
The Baltic countries, Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania, share a rich history and culture. However, if you’re seeking sun-soaked beaches and crystal-clear waters, you may want to venture to the Balearic Islands. This archipelago off the coast of Spain is renowned for its picturesque landscapes and vibrant nightlife.
While the Balearic Islands offer a different experience, the Baltic countries remain captivating destinations with their charming medieval towns, stunning architecture, and welcoming locals.
Key Industries
Key industries driving economic growth in the Baltic countries include:
- IT and Telecommunications: Estonia is a hub for tech startups and digital innovation, while Lithuania excels in fintech and software development.
- Tourism: Riga, Tallinn, and Vilnius attract millions of tourists annually, contributing to the hospitality and service sectors.
- Manufacturing: Lithuania specializes in electronics and machinery, while Latvia has a strong automotive industry.
- Agriculture: Estonia and Latvia have developed modern agricultural sectors, focusing on dairy, livestock, and crop production.
Political Landscape: Baltic Countries
The Baltic countries of Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania have established stable democratic political systems since regaining their independence in 1991. Each country features a parliamentary republic with a multi-party system and a separation of powers between the executive, legislative, and judicial branches.
The constitutions of all three countries guarantee fundamental rights and freedoms, including freedom of speech, assembly, and religion. They also establish the principles of rule of law and the separation of powers.
Political Parties and Ideologies
The political landscapes of the Baltic countries are characterized by a diverse range of political parties representing a wide spectrum of ideologies.
- In Estonia, the two main political parties are the center-right Reform Party and the center-left Centre Party.
- In Latvia, the largest political party is the center-right New Unity party, followed by the center-left Harmony party.
- In Lithuania, the two main political parties are the center-right Homeland Union – Lithuanian Christian Democrats and the center-left Social Democratic Party of Lithuania.
Other notable parties in the Baltic countries include the Estonian Conservative People’s Party, the Latvian National Alliance, and the Lithuanian Liberal Movement.
The Baltic countries of Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania are known for their charming medieval architecture, stunning natural beauty, and rich cultural heritage. If you’re planning a trip to this captivating region, consider using the amex platinum card to enhance your experience.
With its exclusive benefits and rewards, the amex platinum card can help you maximize your travel, from booking flights and accommodations to enjoying unforgettable dining and entertainment experiences. As you explore the Baltic countries, you’ll discover a wealth of historical sites, picturesque landscapes, and vibrant cities that will leave you with lasting memories.
Electoral Systems and Voting Patterns
The Baltic countries use different electoral systems for their parliamentary elections.
- Estonia uses a proportional representation system, where voters cast their ballots for political parties rather than individual candidates.
- Latvia uses a mixed electoral system, combining proportional representation with single-member constituencies.
- Lithuania uses a single-member constituency system, where voters elect individual candidates to represent their districts.
Voter turnout in the Baltic countries is generally high, with Estonia consistently having the highest turnout rate among the three countries.
Foreign Relations

The Baltic countries share a common history, culture, and geopolitical position, which has shaped their foreign policy priorities. They seek to maintain their independence, sovereignty, and territorial integrity, while also fostering regional cooperation and integration.
Relationships with Neighboring Countries
The Baltic countries have close relationships with their Nordic and Baltic Sea neighbors, such as Sweden, Finland, Poland, and Germany. They cooperate on a wide range of issues, including trade, energy, security, and environmental protection. The Baltic Sea region is a key area of focus for the Baltic countries, and they are committed to promoting stability and prosperity in the region.
European Union Membership
The Baltic countries are all members of the European Union (EU), and they see EU membership as a cornerstone of their foreign policy. They believe that EU membership provides them with economic benefits, security guarantees, and a voice in international affairs. The Baltic countries are active participants in the EU, and they contribute to EU decision-making on a wide range of issues.
Role in International Organizations
The Baltic countries are also active members of other international organizations, such as the United Nations, the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE), and NATO. They cooperate with these organizations to promote peace, security, and democracy around the world. The Baltic countries are also committed to promoting human rights and the rule of law, both at home and abroad.
Social and Cultural Trends
The Baltic countries share a rich and diverse cultural heritage, with influences from both Western and Eastern Europe. The region has a strong emphasis on education, healthcare, and social welfare, and boasts a vibrant cultural scene.
The Baltic countries have a high literacy rate and a well-educated population. Education is compulsory for all children from the age of 7 to 18, and there are numerous universities and colleges offering a wide range of academic programs. The region also has a strong tradition of healthcare, with universal access to healthcare for all citizens.
Social Welfare Programs
The Baltic countries have a comprehensive social welfare system that provides a safety net for those in need. The system includes unemployment benefits, social assistance, and pensions for the elderly and disabled. The region also has a strong emphasis on family values, and there are a number of programs in place to support families with children.
Cultural Events and Traditions
The Baltic countries are home to a number of cultural events and traditions. Some of the most popular events include the Song and Dance Festival, which is held every five years in Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania, and the Midsummer Festival, which is celebrated on June 24th.
Last Point
As we bid farewell to our exploration of the Baltic countries, we are left with a profound appreciation for their resilience, innovation, and unwavering spirit. These nations stand as beacons of progress, showcasing the transformative power of collaboration, determination, and the pursuit of a brighter future.
FAQ Guide
What are the official languages of the Baltic countries?
Estonian, Latvian, and Lithuanian are the official languages of Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania, respectively.
What is the largest city in the Baltic region?
Riga, the capital of Latvia, is the largest city in the Baltic region.
Are the Baltic countries part of the European Union?
Yes, Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania joined the European Union in 2004.